PV THERMAL IMAGING
Photovoltaic solar panels constitute a large part of the solar power plant investment amount. At the same time, many performance and safety tests are applied to these solar panels by the relevant laboratories as there are many types of defects that cannot be seen by the eye.
Unlike many other inspection methods, the use of thermal imaging in photovoltaic systems allows the identification of problem panels and cells while the system is in operation; thermal imaging does not require disconnection of the system or any part of it, as it can be performed under normal operating conditions. In addition, thermal inspection can be performed in a shorter time than other inspection methods.
What are the Advantages of Thermal Examination?
- Quality Assurance of Photovoltaic Panel Installation
The quality of photovoltaic panels may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer or even from batch to batch for the same factory. Photovoltaic panels may come out of the factory without any defects and problems, but problems and defects occur even during shipment to the field due to improper loading on transportation vehicles.
The quality of the installation also depends on the skill and competence of the EPC team deployed by the contractor. In short, thermal imaging is one of the easiest ways to keep track of the panels produced, shipped and installed.
- Preventing Electrical Efficiency Losses
When preparing the financial feasibility studies of SPP projects, the project lifetime is assumed to be between 20-25 years and the gradual decrease in the efficiency of the panels is taken into account in such studies. However, as we mentioned in detail earlier, it is difficult to predict the problems that may occur in the panels during transportation and installation or various problems that may occur in the panels during operation and maintenance.
Therefore, a thermal inspection of the stations should generally be carried out at regular intervals to ensure that the stations operate efficiently and are free from faults. For example, every 6 months or once a year. This check is considered one of the routine checks performed by the operation and maintenance (O&M) team.
- Fire Risk Reduction
Thermal imaging in SPP projects is not limited to photovoltaic panels. It is possible to detect and identify any temperature increase in any component of the system with thermal inspection. For example, thermal imaging of electrical panels can detect any problems in cable connections that may cause high temperatures or electrical sparks that may cause fire.

- Fast Identification of Problems
Thermal imaging enables rapid detection and investigation of problems without the need for contact. Most modern thermal cameras record two images, one thermal and one visual.
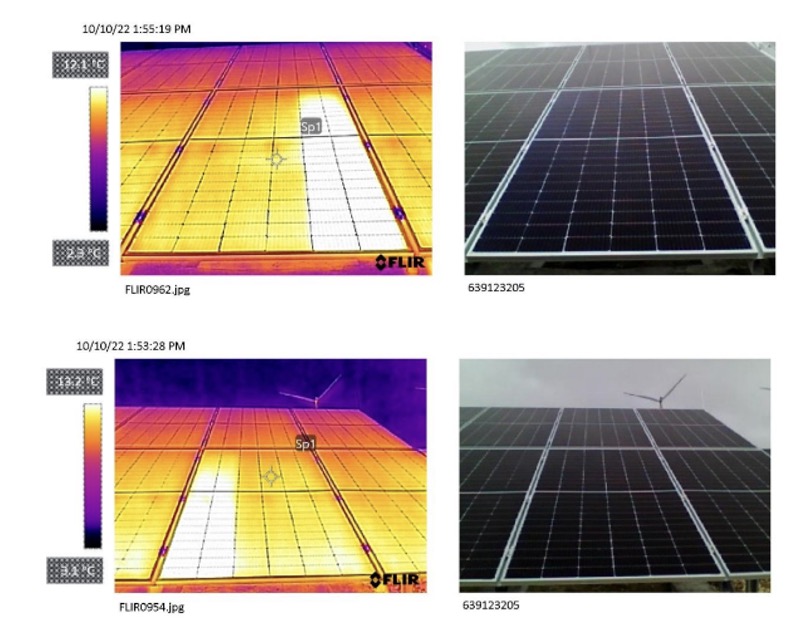

What kind of defects can we detect with thermal inspection?
Thermal imaging aims to identify where there are anomalous temperatures, i.e. where there is a clear temperature difference between one region and another with the same characteristics. Areas with high temperatures in photovoltaic panels are called “Hot Spots”.
So how are these hot spots formed?
Hot spots can simply be caused by shadow falling on solar panels and cells or by manufacturing defects.
- Broken glass
Fractures in the glass of the photovoltaic panel cause the cells to overheat.
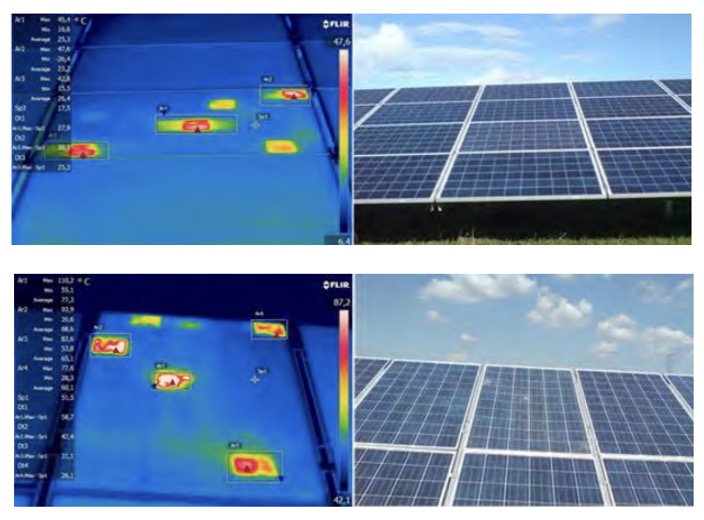

- Shadowing:
Shading is the most common cause of high operating temperature of panels. For example; grass, trees, bird droppings, surrounding tall buildings and poles, etc.
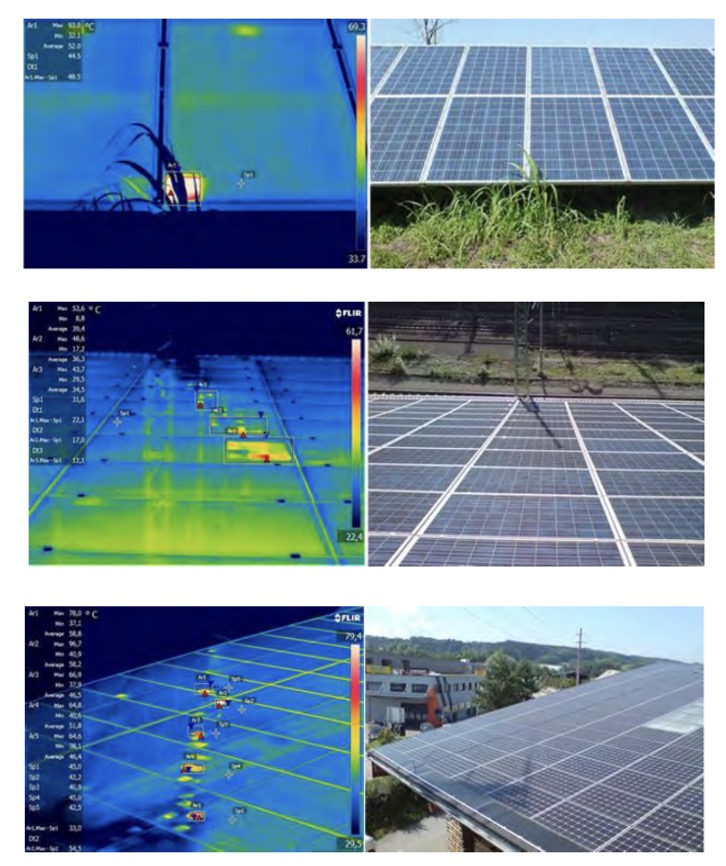
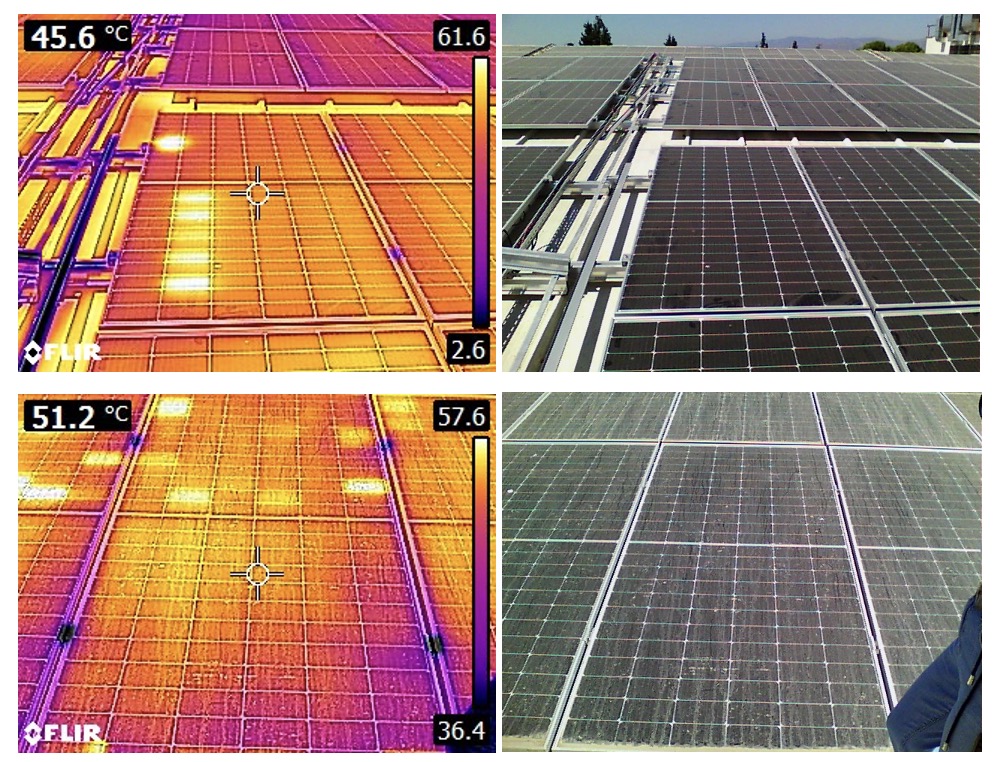
- Production-related problems:
One of the reasons for the high temperatures of photovoltaic panels is defects in the production phase. For example, cells of different efficiency used in the same panel, active and inactive fractures in the panel, poor soldering of ribbons. All such defects will cause hot spots in photovoltaic panels in the long run.
- Overheating of By- Pass Diodes
The junction boxes of PV modules are slightly hotter than the rest of the module. This temperature is caused by overheated bypass diodes inside the junction box. To reduce the effect of shading on the panels on the generation, a bypass diode is connected in parallel and of opposite polarity to an array of solar cells. Under normal operating conditions, the bypass diodes are in reverse polarity mode, i.e. inactive. However, if there is a mismatch between the cells or partial shading affecting the PV panel, the bypass diode switches to forward polarity mode and becomes active. For example, it allows current to flow through it and not through the shaded cell. Therefore, the temperature of the diode when it is active is higher than that of inactive diodes.
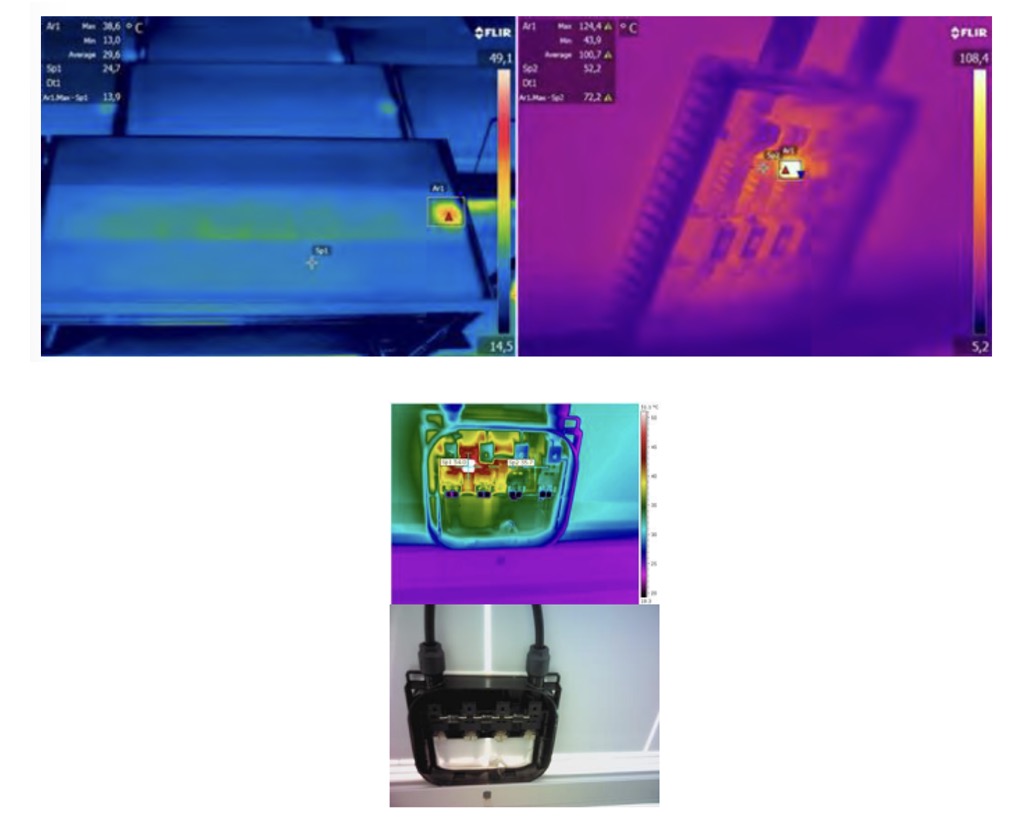
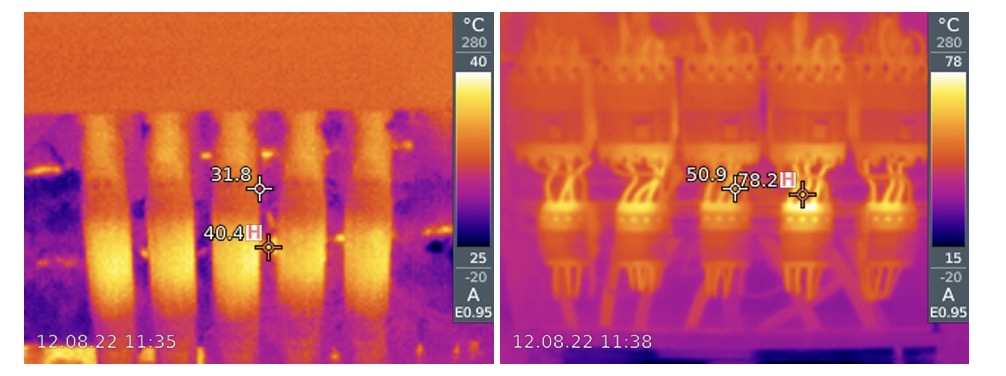
- Overheating of electrical panel connections
Large-scale SPPs usually use centralized inverters with DC collection boxes. Collection boxes are used to collect individual DC strings and connect them to a single larger cable. These aggregation boxes often have thermal problems due to improper wiring, internal cross and loose wiring.
Global Standards in Thermal Imaging
IEC 62446-3 is the standard that determines many environmental conditions and specifications such as equipment (thermal camera), minimum radiation, maximum wind speed to be used in thermal inspection.
The IEC 60904-12-1 standard covers the specifics of thermal inspection of photovoltaic panels in laboratories or production lines, but does not address grid-connected installed SPP system inspections.
Can We Detect All Problems in Panels with Thermal Imaging?
Thermal imaging only detects problems that cause high temperatures. But defects that have not yet caused a temperature rise cannot be detected by thermal imaging.
These undetected defects are often micro-fractures in photovoltaic panels. Electroluminescence imaging can detect these fractures before they become hot spots. We will talk about such examinations in detail in a new article.
Sources:
IEC 62446-3
Report IEA-PVPS T13-10:2018
Author:
